SDG 2: Zero Hunger
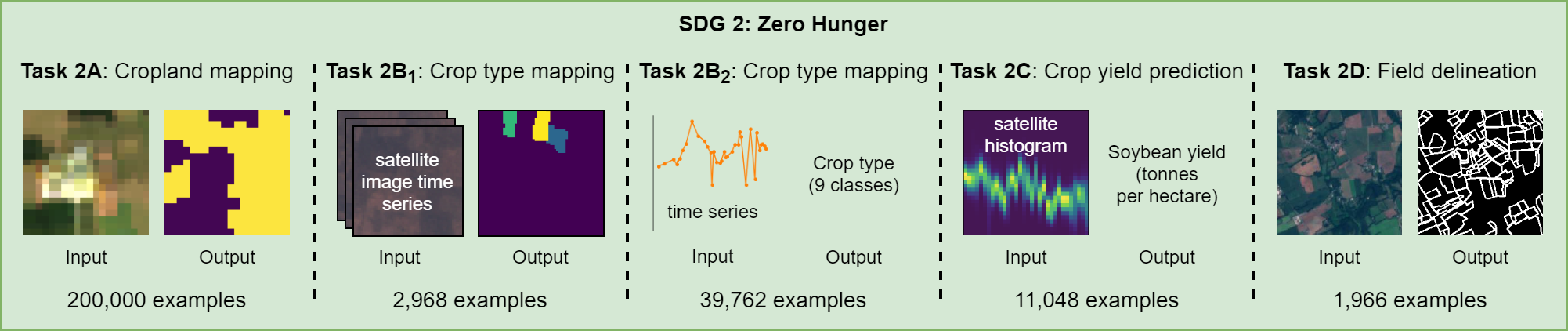
The number of people who suffer from hunger has been on the rise since 2015, with 690 million or 9% of the world’s population affected by chronic hunger [1]. At the same time, 40% of habitable land on Earth is already devoted to agricultural activities and is by far the largest human impact on the natural landscape [2]. The second SDG is to “end hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition, and promote sustainable agriculture.” In addition to ending hunger and malnutrition in all forms, the targets under SDG 2 include doubling the productivity of small-scale food producers and promoting sustainable food production [1]. While traditionally data on agricultural practices and farm productivity are obtained via farm surveys, such data are rare and often of low quality [3], and satellite imagery offers the opportunity to monitor agriculture more cheaply and more accurately. In particular, remote sensing can be used to map cropland, crop types, crop yields, field boundaries, and agricultural practices like cover cropping and conservation tillage.
The SustainBench datasets for SDG 2 are summarized below.
References
[1] United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2021. The Sustainable Development Goals Report. United Nations, 2021 edition, 2021. ISBN 978-92-1-005608-3. doi: 10.18356/9789210056083. URL https://www.un-ilibrary.org/content/books/9789210056083.
[2] Food and Agriculture Statistics, 2021. URL http://www.fao.org/food-agriculture-statistics/en/.
[3] M. Burke, A. Driscoll, D. B. Lobell, and S. Ermon. Using satellite imagery to understand and promote sustainable development. Science, 371(6535), 2021. doi: 10.1126/science.448abe8628. URL https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abe8628.